Abstract Cryopreservation bags are specialized, flexible containers engineered for the safe, reliable low-temperature storage of biological samples, ranging from cells, tissues, and blood products to vaccines and gene therapy vectors. Distinguished by their superior biocompatibility, structural integrity under extreme cryogenic conditions, and compatibility with automated sample processing workflows, cryopreservation bags have gradually replaced traditional rigid cryovials in large-scale biological sample banks, clinical research, and biopharmaceutical production. This paper systematically elaborates on the material composition, structural design, and full-process application advantages of cryopreservation bags, covering sample pre-processing, cryopreservation, long-term storage, thawing recovery, and traceability management. It also analyzes their core performance characteristics and compliance standards, providing a comprehensive technical reference for researchers and practitioners in the fields of biomedicine, cell therapy, and biological sample management.
1. Introduction
The long-term preservation of biological samples is a cornerstone of modern biomedicine, clinical diagnostics, and biopharmaceutical research. High-quality sample storage directly determines the reproducibility of experimental results, the success of cell therapy products, and the safety of vaccine development. Traditional sample storage relies on rigid cryovials made of glass or polypropylene; however, these containers have inherent limitations, including limited capacity, high risk of breakage under liquid nitrogen conditions, low space utilization efficiency, and difficulty in integrating with automated sample handling systems.
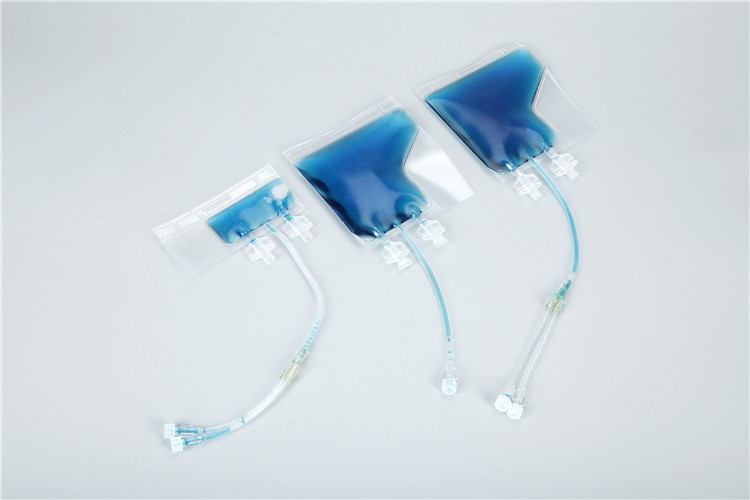
Against this backdrop,
cryopreservation bags have emerged as a full-process solution for low-temperature sample storage. Designed with flexible, cryo-resistant materials and advanced sealing technology, these bags address the pain points of traditional storage methods while meeting the stringent requirements of large-scale, high-throughput sample management. With the rapid development of cell therapy, regenerative medicine, and precision medicine, cryopreservation bags have become an indispensable core tool in biological sample storage systems.
2. Material Composition and Structural Design of Cryopreservation Bags
The performance of cryopreservation bags is fundamentally determined by their material selection and structural design, which are optimized to withstand extreme low temperatures (as low as -196°C in liquid nitrogen) and maintain sample integrity.
2.1 Core Material Characteristics
Cryopreservation bags are primarily fabricated from medical-grade flexible polymers, with strict compliance with biocompatibility and safety standards:
1. Medical-Grade Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
PVC is the most widely used material for cryopreservation bags, characterized by excellent flexibility, low-temperature resistance, and gas impermeability. Medical-grade PVC is free of plasticizers such as DEHP, ensuring no leaching of harmful substances into the sample. It remains ductile at -196°C, avoiding embrittlement and cracking that are common with rigid materials.
2. Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG)
PETG is a high-performance copolymer with superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance compared to PVC. It is suitable for storing samples sensitive to PVC additives, such as stem cells and gene therapy vectors. PETG bags exhibit excellent dimensional stability during freeze-thaw cycles and can be sterilized by gamma irradiation without degradation.
3. Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA)
EVA is a soft, flexible polymer with exceptional low-temperature toughness and biocompatibility. EVA-based cryopreservation bags are ideal for long-term storage in liquid nitrogen vapor phase, as they resist swelling and deformation under prolonged cryogenic exposure.
2.2 Structural Design Optimization
The structural design of cryopreservation bags is tailored to the full-process needs of biological sample handling:
1. Multi-Layer Sealing Structure
The bags adopt a heat-sealed edge design with double or triple sealing layers, ensuring leak-proof performance even under high internal pressure during freezing (caused by sample volume expansion). The seal strength is tested to withstand ≥ 50 kPa of internal pressure, preventing sample contamination and cross-contamination.
2. Integrated Access Ports
Most cryopreservation bags are equipped with one or more sterile access ports, including injection ports for adding cryoprotectants and sampling ports for aseptic sample retrieval. These ports are sealed with self-sealing rubber stoppers or Luer lock connectors, compatible with standard laboratory syringes and automated liquid handling systems.
3. Graduated Markings and Labeling Areas
Clear volume markings (ranging from 1 mL to 500 mL, or even 1000 mL for industrial-scale applications) are printed on the bag surface for accurate sample dispensing. A dedicated, frost-resistant labeling area is designed to accept barcode or RFID tags, enabling traceability of sample information throughout storage and handling.
4. Anti-Burst and Space-Saving Design
The flat, flexible structure of cryopreservation bags maximizes storage space utilization—up to 3 times more samples can be stored per unit volume compared to rigid cryovials. Reinforced corners and thickened bottom layers reduce the risk of burst during rapid freezing and thawing.
3. Full-Process Application of Cryopreservation Bags in Biological Sample Storage
Cryopreservation bags provide a seamless, end-to-end solution covering every stage of biological sample management, from pre-processing to thawing and recovery, with distinct advantages over traditional storage containers at each step.
3.1 Sample Pre-Processing and Dispensing
1. Aseptic Filling
Cryopreservation bags are supplied in a sterile, ready-to-use state, eliminating the need for pre-sterilization and reducing the risk of sample contamination. The wide opening design of large-capacity bags facilitates manual or automated filling of samples, such as cell suspensions, blood plasma, or vaccine formulations. For sensitive cells, the bags can be connected directly to bioreactors via sterile tubing, enabling closed-system transfer and minimizing exposure to ambient air.
2. Cryoprotectant Addition
The integrated access ports allow for the aseptic addition of cryoprotectants (e.g., DMSO, glycerol) without opening the bag. This closed-system operation prevents the introduction of contaminants and ensures uniform mixing of the cryoprotectant with the sample, critical for maintaining cell viability during freezing.
3.2 Controlled Freezing Process
1. Gradient Cooling Compatibility
Cryopreservation bags are compatible with standard controlled-rate freezers, which reduce the temperature at a precise rate (typically -1°C/min) to form small ice crystals, avoiding cell damage caused by rapid freezing. The flexible structure of the bags ensures uniform heat transfer, preventing localized supercooling and ice crystal formation that can harm sensitive cells like stem cells.
2. Direct Liquid Nitrogen Freezing
For samples requiring ultra-rapid freezing, cryopreservation bags can be directly immersed in liquid nitrogen (LN₂) or placed in the LN₂ vapor phase. The low-temperature-resistant materials maintain structural integrity, and the sealed design prevents LN₂ from entering the bag and diluting the sample.
3.3 Long-Term Cryogenic Storage
1. Liquid Nitrogen Vapor Phase Storage
The preferred storage method for most biological samples, the vapor phase (temperature range: -150°C to -190°C) avoids direct contact between the bag and LN₂, reducing the risk of contamination and bag damage. Cryopreservation bags are stackable, maximizing the storage capacity of LN₂ freezers and sample banks.
2. Automated Storage and Traceability
The barcode/RFID labeling area on the bag surface enables seamless integration with laboratory information management systems (LIMS). Automated sample storage systems can identify, sort, and retrieve bags without manual intervention, improving the efficiency of large-scale sample banks and reducing human error.
3.4 Thawing and Sample Recovery
1. Rapid, Uniform Thawing
The thin, flexible walls of cryopreservation bags allow for rapid heat transfer during thawing. Bags can be immersed in a 37°C water bath, and the sample can be completely thawed within minutes—faster than rigid cryovials, which often suffer from uneven thawing (resulting in cell death). The closed-system design during thawing prevents sample contamination, a critical advantage for clinical-grade cell therapy products.
2. Aseptic Sample Retrieval
After thawing, samples can be retrieved aseptically via the access ports without opening the bag, minimizing the risk of microbial contamination. For large-volume bags, multiple access ports enable simultaneous sampling and transfer, supporting high-throughput experimental workflows.
4. Core Performance Advantages of Cryopreservation Bags
Compared to traditional rigid cryovials and glass containers, cryopreservation bags offer unique technical and operational advantages:
4.1 Superior Biocompatibility and Sample Safety
Medical-grade materials used in cryopreservation bags comply with ISO 10993 and USP Class VI standards, ensuring no cytotoxicity, hemolysis, or leachable substances. This makes them suitable for storing clinical-grade samples, such as CAR-T cells, hematopoietic stem cells, and vaccines, where sample safety is paramount.
4.2 High Structural Integrity Under Cryogenic Conditions
The flexible polymer materials maintain their toughness at -196°C, eliminating the risk of breakage that is common with glass vials and polypropylene cryovials. The multi-layer sealing structure prevents leaks even after repeated freeze-thaw cycles, ensuring sample integrity over long-term storage (up to 10 years or more).
4.3 High Space Utilization and Cost-Effectiveness
The flat, stackable design of cryopreservation bags increases storage space utilization by 200–300% compared to rigid cryovials. For large-scale sample banks and biopharmaceutical production, this translates to significant cost savings in freezer capacity and facility space.
4.4 Compatibility with Closed-System Workflows
Cryopreservation bags support closed-system sample handling, from bioreactor harvest to storage and thawing. This closed workflow is essential for clinical applications, as it reduces the risk of contamination and meets the GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) requirements for cell therapy and vaccine production.
4.5 Easy Traceability and Management
The integrated labeling area and compatibility with barcode/RFID technology enable full traceability of sample information, including batch number, storage date, and freezing protocol. This is critical for regulatory compliance in biopharmaceutical and clinical research settings.
5. Typical Application Scenarios
Cryopreservation bags are widely used in various fields of biomedicine and biopharmaceuticals, driven by their full-process storage capabilities:
5.1 Cell Therapy and Regenerative Medicine
Cryopreservation bags are the gold standard for storing clinical-grade cell products, such as CAR-T cells, mesenchymal stem cells, and hematopoietic stem cells. The closed-system workflow ensures compliance with GMP regulations, while the high biocompatibility preserves cell viability and function during long-term storage.
5.2 Vaccine and Biopharmaceutical Production
Large-capacity cryopreservation bags (50–1000 mL) are used to store vaccine bulk, monoclonal antibodies, and gene therapy vectors. Their compatibility with automated filling and freezing systems makes them ideal for industrial-scale production, improving efficiency and reducing labor costs.
5.3 Clinical Sample Banks
Hospitals and research institutions use cryopreservation bags to store human biological samples, such as blood, tissue biopsies, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). The stackable design and traceability features simplify sample management, enabling rapid retrieval for diagnostic and research purposes.
5.4 Agricultural and Environmental Biotechnology
Cryopreservation bags are used to store plant seeds, microbial cultures, and algae strains for agricultural breeding and environmental remediation research. The low-temperature resistance and leak-proof design ensure the long-term preservation of these valuable biological resources.
6. Quality Control and Regulatory Compliance
To ensure the safety and reliability of cryopreservation bags, strict quality control and compliance with international standards are essential:
1. Sterility Testing: All cryopreservation bags undergo gamma irradiation sterilization (25–50 kGy) and are tested for sterility according to ISO 11737, ensuring no microbial contamination.
2. Leakage Testing: Each bag is subjected to pressure testing (≥ 50 kPa) to verify leak-proof performance, preventing sample loss and cross-contamination.
3. Biocompatibility Testing: Compliance with ISO 10993 (cytotoxicity, sensitization, irritation) and USP Class VI standards is mandatory for medical and clinical applications.
4. Regulatory Compliance: Cryopreservation bags used in clinical trials and biopharmaceutical production must meet the requirements of the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) and EMA (European Medicines Agency), including documentation of material composition and manufacturing processes.
7. Future Development Trends
As biomedicine and biopharmaceutical technology advance, cryopreservation bags are evolving toward smarter, more specialized designs:
1. Intelligent Traceability: Integration of passive RFID tags or temperature-sensitive indicators (TSIs) to monitor storage temperature in real time, alerting users to temperature fluctuations that may compromise sample integrity.
2. Specialized Material Development: Research into biodegradable polymers and oxygen-impermeable films to extend sample storage life and reduce environmental impact.
3. High-Throughput Automation Compatibility: Design of bags with standardized dimensions and connection ports to integrate with next-generation automated sample handling systems, supporting the large-scale storage needs of precision medicine.
8. Conclusion
Cryopreservation bags have revolutionized the low-temperature storage of biological samples by providing a safe, efficient, and compliant full-process solution. Their advanced material composition, structural design, and compatibility with closed-system workflows address the limitations of traditional storage containers, making them indispensable in cell therapy, vaccine development, clinical sample banking, and biopharmaceutical production. As regulatory requirements for biological sample management become increasingly stringent and the demand for large-scale sample storage grows, cryopreservation bags will continue to play a central role in advancing biomedicine and biopharmaceutical innovation.
